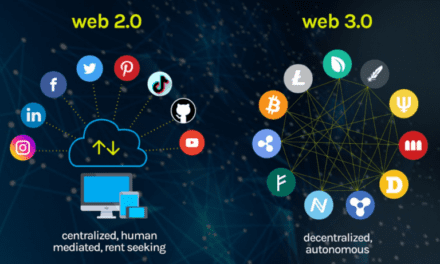
Web 3.0 is not a single technology but a combination of powerful innovations working together to create a decentralized digital ecosystem. Understanding these technologies helps explain why Web 3.0 is such a major shift from the traditional internet.
The foundation of Web 3.0 is blockchain technology. A blockchain is a distributed ledger that records transactions across many computers. Once data is added, it cannot be altered easily, ensuring transparency and security. Popular blockchains like Ethereum, Solana, and Polkadot support thousands of decentralized applications.
Web 3.0 technologies
Next are cryptocurrencies, which act as the native financial layer of Web 3.0. Unlike traditional money, cryptocurrencies enable peer-to-peer value transfer without banks. They also serve as incentives for network participants, such as miners or validators, who secure the blockchain.
Smart contracts are one of the most revolutionary Web 3.0 technologies. These programs automatically execute when predefined conditions are met. For example, in decentralized finance (DeFi), smart contracts can handle lending, borrowing, and trading without human intervention.
Another key element is decentralized applications (dApps). These apps look similar to traditional apps but operate on blockchain networks. Examples include decentralized exchanges, NFT marketplaces, and blockchain-based games. dApps eliminate the need for centralized control while maintaining transparency.
Decentralized storage is also essential. Instead of relying on centralized servers like Amazon or Google, Web 3.0 uses systems such as IPFS and Arweave to store data across multiple nodes. This improves data permanence and censorship resistance.
Identity management in Web 3.0 is handled through crypto wallets. A wallet serves as your login, payment method, and digital identity. Users control their credentials rather than handing them over to platforms.
Finally, oracles play a crucial role. Blockchains cannot access real-world data on their own, so oracles feed external information like prices, weather, or sports results into smart contracts.
Together, these technologies create an internet that is open, permissionless, and user-owned. While still evolving, they form the backbone of Web 3.0’s promise.